Innovation Summary
 Kenya’s Ugunja Community Resource Center will empower community health volunteers in Western Kenya with field-tested, mobile phone software to individualize early child development care in the family home and monitor progress via the cloud based server.
Kenya’s Ugunja Community Resource Center will empower community health volunteers in Western Kenya with field-tested, mobile phone software to individualize early child development care in the family home and monitor progress via the cloud based server.
The software suite will include “apps” for community health workers, for parents and for caregivers. These apps will offer practical advice, tools, educational aids as well as forms for assessing and fostering early childhood development, including: cognitive development, nutritional support, management of common illnesses, and counseling on cognitive stimulation for parents and caregivers.
The online monitoring program features a “dashboard” to help users visualize key processes, performance indicators and outcome metrics. An analytics suite will enable program managers to analyze trends in data collected.
Gallery
Impact Summary
- 30 community health volunteers will be trained.
- 942 households with at least one child under age 3 will be served.
- 10 parents will have improved knowledge on ECD and positive care practices.
Innovation
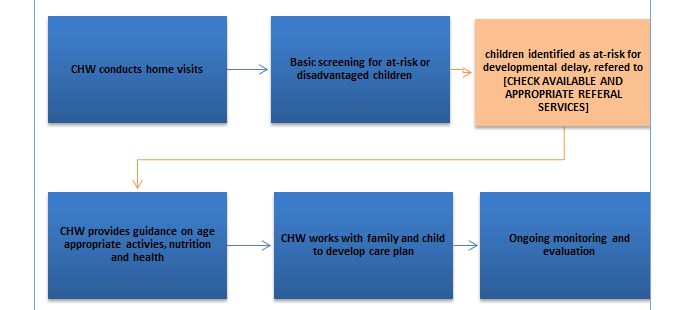
The innovation will create opportunities for community members to play a critical role in improving child outcomes. This innovation integrates into the existing community health volunteers (CHVs) within the community, who will be trained on a new Early Childhood Development (ECD) training module designed based on development science and allowing for local adaptations. Training programs for CHVs are developed in collaboration with local health practitioners along adult-learning theories. The content of the training includes basic cognitive and socio-cultural processes, and strategies to address developmental delays and the underlying causes of developmental delays, including nutrition and stimulation. The content also has components on effective communication strategies for working with parents of disadvantaged children. The newly-equipped cadre of CHVs, d with skills and tools to promote improved child development outcomes, will be integrating these skills alongside their other routine health outcome monitoring in households, which includes collecting health monitoring data.
The innovation uses Mobile Tools and support systems through CommCare. This aspect seeks to identify children that may be at-risk for delays, so that future interventions and services can be planned accordingly, including ECD modules. This innovation is a pilot, to determine cut-off points for children identified as being at risk for delay across the domains of cognitive skills, executive function, fine and gross motor skills, language and social/ emotional development. referral services to local clinics or specialists will be advised for children who are identified during CHV home visits or through developmental screenings as in need of additional support.
Collaboration
Funders
- Grand Challenges Canada
Key Partners
- Harvard Business School and Dimagi Inc. of Cambridge MA
- University of Pennsylvania
- Kenya Methodist University School of Medicine and Health of Kenya
- St. Pauls’ Methodist Hospital
- Kenya Ministry of Health (MOH)
Implementation
Key Drivers
Use of existing and accessible resources:
- Use of existing National Human Resource for health framework under the Ministry of Health.
- Use of an open source platform to develop the “app”.
Training and equipping the existing cadre of CHVs with skills and tools to promote improved child development outcomes.
Challenges
Restructuring of the CHVs workforce.
Continuation
The innovation has the potential to replace paper-based reporting for the ministry of health, which less accurate as a mobile or online “app”. This potential is supported by the current activities of the government of Kenya, who are undertaking efforts to digitize all their systems, and the Ministry of Health in Kenya, who has devolved a system of health information to which data can be uploaded using automated systems. The project team will develop a Policy brief containing summary of results and recommendations for scale-up, directed to the Kenyan Ministry of Health and Ministry of Education, as well as wider policy audience.
Evaluation Methods
The intervention will be evaluated through the following critical milestones;
- % change in children under age 3 within the project catchment area scoring below age-expected range on ECD screening scores in one or more domains (estimated 50% at baseline to 25% at endline).
- # of children under age 3 within the project catchment area who are visited by a CHV and screened using CommCare:ECD during the project period.
- # of CHVs trained in CommCare:ECD.
Impact of Innovation
- 471 households with at least one child under 3 will have access to the products and services.
- 30 CHVs will be trained and equipped with tools to support care givers on ECD.
- 3 jobs created (Deputy Project Manager and two CHV Supervisors).
- 3 innovative prototypes of service delivery models developed.
- Policy brief containing summary of results and recommendations for scale-up, directed to Kenya Ministry of Health and Ministry of Education, as well as wider policy audience.
Cost of Implementation
The cost needed for this project is for development of the tools, This is one time cost, after all is done, what is left is just monitoring and support.
Resources
-
Research
-
Bhutta, Z. A. et al. (2008). Interventions to address maternal, newborn, and child survival: What difference can integrated primary health care strategies make? The Lancet, 372(9642), 972—989.
-
Black, R. E., et al. (2008). Maternal and child undernutrition: Global and regional exposures and health consequences. The Lancet, 371(9608), 243—260.
-
DeRenzi, B., et al. (2011). Mobile phone tools for field-based health care workers in low-income countries. Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine: A Journal of Translational and Personalized Medicine, 78(3), 406–418.
-
Engle, P. L., et al. (2007). Strategies to avoid the loss of developmental potential in more than 200 million children in the developing world. The Lancet, 369(9557), 229—242.
-
Fernald, L. C. H., et al. (2009). Examining early child development in low-income countries: A toolkit for the assessment of children in the first five years of life. The World Bank, Washington.
-
Jones, G., et al. (2003). How many child deaths can we prevent this year? The Lancet, 362(9377), 65—71.
-
Grantham-‐McGregor, S., et al. (2007). Developmental potential in the first 5 years for children in developing countries. The Lancet, 369(9555), 60—70.
-
Haines, A., et al. (2007). Achieving child survival goals: Potential contribution of community health workers. The Lancet, 369(9579), 2121—2131.
-
Lehmann, U., Sanders, D. (2007) Community health workers: What do we know about them? The state of the evidence on programmes, activities, costs and impact on health outcomes of using community health workers. Department of Human Resources for Health, Evidence and Information for Policy, World Health Organization. Geneva.
-
Lewin, S., et al. (2010). Lay health workers in primary and community health care for maternal and child health and the management of infectious diseases. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 3.
-
Linsk, N., et al. (2010). Para-social work to address most vulnerable children in sub-‐sahara africa: A case example in tanzania. Children and Youth Services Review, 32(7), 990-‐997.
-
Shonkoff, J. P. (2010). Building a new biodevelopmental framework to guide the future of early childhood policy. Child Development, 81(1), 357–367.
-
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). (2010). Progress for children: reaching the MDGs with equity. UNICEF, New York.
-
(2008). State of the world’s children. UNICEF, New York.
-
Walker, S. P., et al. (2007). Child development: Risk factors for adverse outcomes in developing countries. The Lancet, 369(9556), 145—157.
-
Walley, J., et al. (2008). Primary health care: Making alma-ata a reality. The Lancet, 372(9642), 1001—1007.
-
World Health Organization (WHO). (1989). Strengthening the Performance of Community Health Workers in Primary Health Care. Report of a WHO Study Group. Technical Report Series 780.
-
You, D., et al. (2010). Levels and trends in under-5 mortality, 1990–2008. The Lancet, 375(9709), 100—103.
-
-
Key Reports
-
Instruments & Batteries
-
PEDS: DM. Language.
-